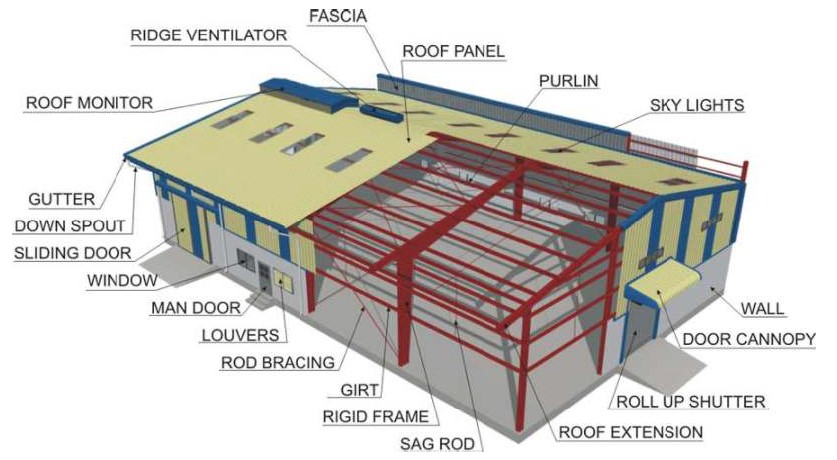
While designing any new roof or renovating existing roof, it is important to check all technical parameters to attain perfection. A well-designed roof is an ideal solution to safeguard us from extreme weather conditions and all-natural calamities.
Being the most essential part of any industrial building, roofing is a vital component which needs to be maintained with stability and carried appropriately. In the current trend most of the Metal Buildings are designed with shallow roof slope to get safe and economical building solution. When the roof slope is shallow, there is a negative pressure that develops on the roof which tries to uplift the roof panels.
By choosing the right purlin spacing with a right roof profile, stability in roof is achievable.
What are Purlins?
Purlin is a structural secondary member which forms the skeleton of the Metal Building. Purlins are the longitudinal horizontal members connecting the rafters along the length of the building. The structural support of every building is made up of purlins.
What are the main functions of Purlins?
- Transferring the wind loads to the main frame, rafters and columns. Thus providing structural stability to the main frames by connecting them all along the building.
- Supporting the Roof System i.e. the enclosure of the building.
- Purlins are the structural load carrying members. The wind forces acting on the End Walls of the building get transferred by purlins to the main frame members and to the foundation, by means of bracings.
- Purlins also supports roof system, and are designed to take care of wind load acting on the roof, Live Load, Dead load of Sheeting or roofing and collateral loads like Ventilation duct load, sprinklers, lightings etc.
Thus, Purlins are an important component of the building.
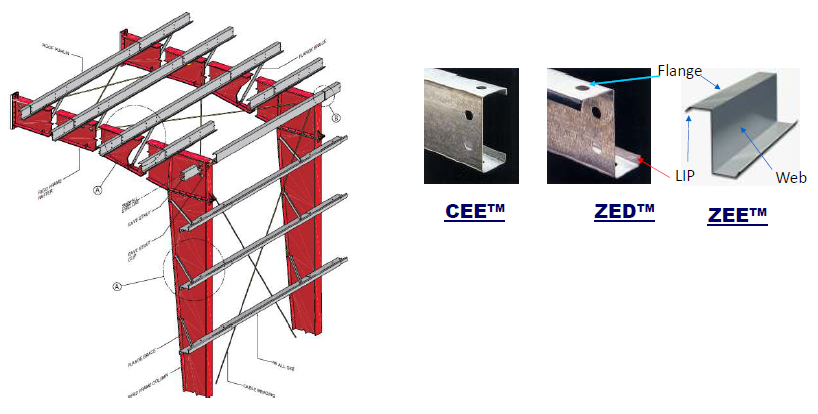
What are the different types of Purlins?
Raw Material wise two types of Purlins are there
- Hot rolled Purlin
- Cold Rolled Purlin
Based on the Shapes
- Circular – pipes / tubes (Hot rolled)
- Square and Rectangular hollow sections (Hot Rolled)
- ZEE, ZED and CEE shaped purlins (Cold formed)
Today, Metal Buildings have evolved with design technology called Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB), with clear span of 90 mtr. Purlins used in these PEBs are of either ZEE or ZED shaped Cold formed members having the min yield strength of 300 MPa. These ZEE or ZED Purlins are of min 1.2mm thickness to maximum 3.15 mm steel thickness. These are generally roll formed from Pre-Galvanized sheets having the zinc coating mass of min 120 GSM to the maximum of 275 GSM.
Factors considered while designing Purlin
While designing any structural member, we need to find the load acting on that member. To determine the load, complete building parameters like Width, Length, Height, Roof Slope and Wind Speed of the building should be considered.
1. Loads acting on the Purlin
Dead Load of roofing systems are self-weight of the roof sheet, Solar modules, roof platforms, ventilators, walkways etc.
Live Load on the roofing system
Wind Load which are external in nature
Collateral loads are the hanging loads from the Purlin
2. Support type
Second important factor is the support type, whether it is supported as a Single Span or Continuous Span by Overlapping the purlins. CEE members are generally used as a simply ‘supported Purlin’ and ZEE or ZED purlins as a continuous span as we can overlap the purlins.
3. Span of the Purlin
Third important factor is the Span of the Purlin, that is the Bay Spacing or Rafter to Rafter spacing. Based on the span, Strength and Deflection of purlin will be determined.
Purlin is designed basis the roof system. For example, if Screw down system is put on top of the Purlin then the screw down profiles provides the Diaphragm which provides bracing strength to Purlins. In case standing seam, profiles are fixed on top of Purlin and then the purlins need to be checked for Lateral Torsional Buckling apart from its bending moment and deflection checks.
Cold formed design codes must be used while designing cold formed purlins.
4. Selection of the Purlin type and Design Optimization
Cold formed ZEE Shaped purlins are most economical solutions nowadays as compared to Hot rolled ISMC channels and other HR pipe purlins. HR Purlins are higher in weights (kg/m). Also, they cannot be overlapped hence need to be designed as a Simply supported section which limits optimization. Whereas Cold formed ZEE purlins are slim and available in the thickness range of 1.2mm to 3.15mm, and can be overlapped for different lengths, resulting in designing of most optimized purlin sections. On an average 30% to 50% weight savings can be achieved using Cold formed ZEE Purlins.
5. Purlin Finish
Cold formed Purlins are roll formed from pre-galvanized Coils with Zn coating mass of minimum 120 GSM to the maximum of 275 GSM. If the environment is controlled and away from coastal and chemical industries like ware houses, small manufacturing units, factories without any generation of chemicals then 120 GSM coating is enough.
For the other chemical and costal environment minimum coating mass of 275 GSM is required. For severe corrosive environments, we can further increase the coating mass of zinc or can apply any anti corrosive paints on the purlins. Alternatively, Purlins can be sealed with false ceiling materials as well.
LYSAGHT® high strength light-weight recyclable purlins – CEE-plus™, ZEE-plus™ & ZED-plus™ provide economy to the building construction and also helps in keeping the site clean and environment friendly.
LYSAGHT® CEE-plus™, ZEE-plus™ & ZED-plus™ sections are accurately roll-formed from high strength zinc-coated steel, pre-punched to the required dimensions to provide an efficient, lightweight, economical purlin and girts.
LYSAGHT® profiles made of COLORBOND® and ZINCALUME® steel manufactured and supplied by Tata BlueScope Steel are suitable for roof, wall support and portal framing up to a certain span. The system, which includes bridging and a comprehensive range of accessories, is supplied as ready for erect.